” The Bonnethead Shark is the apparent shark!”
Of all the fish in the sea conserve those that live where the sunlight does not beam, nature appears to have actually taken unique satisfaction in repositioning the shark over ages. There have actually been sharks with what resemble anvils on their heads and sharks with curlicuing reduced jaws. In modern-day times, there are sharks with heads that resemble hammers or demilunes. The last explains the bonnethead shark, or shovelhead, a little and reluctant fish located in seaside exotic and warm waters.
4 Bonnethead Shark Realities
- The bonnethead is the only omnivorous shark, which suggests it consumes both plants and animals.
- It’s the only shark where you can inform males from females from the top. Females have a smooth rounded head and males have a lump to their head.
- The shovelhead connects with various other shovelheads via exhausts of cerebrospinal liquid.
- Female bonnethead sharks shed their cravings when they deliver. This maintains them from consuming their children.
Bonnethead Shark Classification and Scientific Name
The bonnethead shark’s scientific name is Sphyrna tiburo Sphyrna originates from the Greek for “hammer,” and tiburón is the Spanish word for “shark.” It comes from the Sphyrna genus, which incorporates the hammerhead sharks and the Carcharhiniformes order. A lot of sharks come from this order. They have 2 fins on their back, 5 gill openings, a rectal fin, and eyes that are secured by nictitating membrane layers.
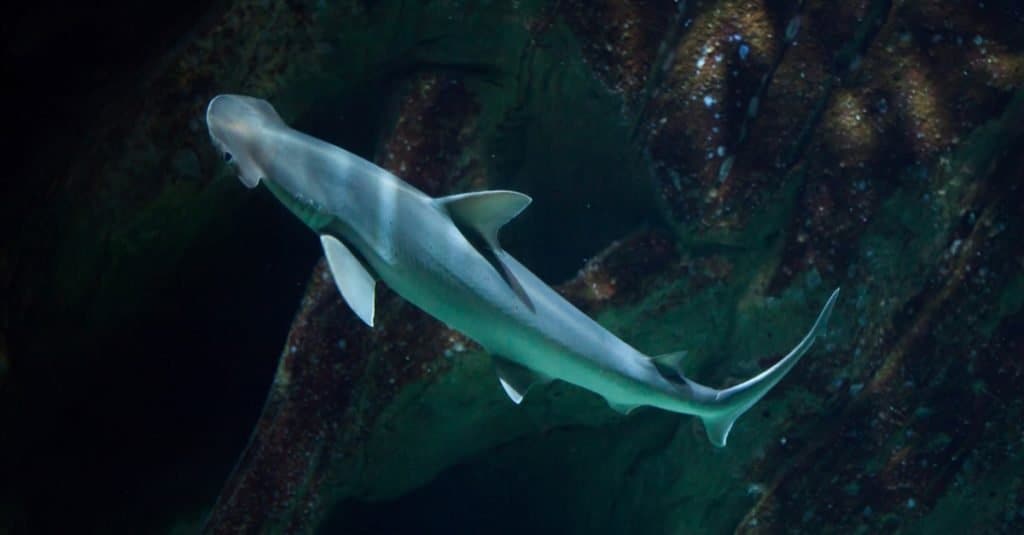
Bonnethead Shark Appearance
One take a look at the bonnethead shark recognizes it immediately. It is the only shark with a demilune- designed head. Its eyes get on either end of its head. The head is smaller sized than those of various other hammerheads, and the rate of this is that the shark is a little bit much less hydrodynamic than its relatives. It needs to roll its head around and utilize its pectoral fins to swim correctly. The hood shark likewise should continuously swim lest it sinks.
Males are 20 to 30 inches in size, while females can expand as huge as 39 inches. They are brownish or green- brownish on the top, and their conceal, made harsh via facial denticles, can be identified. The shark has one huge dorsal fin and a smaller sized one near the tail, a rectal fin, a set of pectoral fins, and a set of pelvic fins. The tail is long, with one lengthy wattle and a much shorter wattle. The teeth of the bonnethead shark are sharp in the front. The back teeth are molars made use of to erode the coverings of the shellfishes it likes.

Vladimir Wrangel/Shutterstock. com
Bonnethead Shark Distribution, Populace, and Environment
The bonnethead is located in the warm and exotic seaside waters off the eastern and western USA, Central America, the Gulf of Mexico, and the Caribbean, off the shore of Ecuador and the eastern shore of South America to Argentina. It can be located in colleges in coral reefs, networks, bays, and tidewaters. It has actually also been located in mudflats.
Though the specific populace is unidentified, the bonnethead shark seems plentiful in the places where it’s located. Though it is not noted on the IUCN red listing since 2021, several researchers think that its conservation status would certainly be Least Concern.
Bonnethead Shark Predators and Target
Though humans do eat the bonnethead shark’s flesh, it is not searched for for human usage. A lot of bonnethead sharks seem inadvertently captured in lines or internet created various other fish.
Various Other predators besides humans consist of bigger sharks such as tiger sharks or great white sharks. The shovelhead is likewise parasitized by a range of microorganisms, consisting of nematodes, copepods, and Myxosporea.
Bonnethead sharks like mollusks and shellfishes, specifically heaven crab, and their teeth are created ordering the victim after that grinding up the coverings. Among the factors the bonnethead relocates its head the method it does as it swims is to pick up victim that might be concealing underneath the sand. It will certainly likewise eat bony fish. The bonnethead is likewise remarkable because it’s the only shark understood that eat plant product. It consumes algae and seagrass. Some researchers think the shark does this to secure its digestive tract versus the sharp sides of crab coverings.
Bonnethead Shark Recreation and Life-span
Researchers do not understand much regarding the breeding habits of bonnethead sharks, however like all sharks, fertilizing is interior. The female might likewise keep the sperm for a couple of months till the moment is ideal for her to conceive. She’ll relocate to an area that’s finest for the puppies, which is superficial water near the coast. When birth takes place likewise depends upon the place and can take place from mid- August to late September. When she is expectant the female bonnethead remains by doing this for just 4 to 5 months. This is a really brief pregnancy duration for a shark.
The female at some point brings to life 6 to 9 puppies each time. At birth, they’re a little over a foot long. They are quickly independent however invest the initial years of their lives shielding in seagrass beds.
Bonnethead Shark in Angling and Food Preparation
The bonnethead shark is a sportfish for some individuals, and though it’s not as searched for for food as the mako or various other sharks, the meat can be dried out, consumed fresh, or became fishmeal.
Bonnethead Shark Populace
Though the populace of these sharks is unidentified, they are plentiful in the areas where they are located.