The blister beetle, additionally called an oil beetle, is a family of plant- consuming insects which have the capability to eliminate a poisonous compound from their joints when really feeling endangered.
This liquid, called cantharidin, can trigger uncomfortable swelling, inflammation, and blistering on the human skin. These signs go away after a number of days, specifically with the application of dermatitis therapy, and seldom leave any type of lengthy- term impacts.
Nonetheless, blister beetles really trigger rather a great deal of damages to plants and plants. They additionally position an extra severe hazard to animals such as horses, livestock, and sheep, which might inadvertently consume huge amounts of cantharidin if it’s ground up in hay. The contaminant, which lingers long after the fatality of the beetle, might trigger inflammation and swelling of the digestive system and urinary system system, and relying on just how much is consumed, there is the opportunity of fatality after regarding 72 hrs. For these factors, it is taken into consideration to be even more of a farming or animals parasite as opposed to an interior parasite.
4 Unbelievable Blister Beetle Realities!
- In lots of species, like the red- headed blister beetle of Arizona, the male beetle will certainly stay affixed to his friend for greater than 24-hour in order to reproduce with each other. The female remains to relocate in between blossoms to feed as she brings him about.
- After mating, the female beetle will certainly hide maybe numerous eggs in the ground and allow them hatch out by themselves. She does not offer any type of adult treatment, however she might layer the eggs with a little bit of her very own contaminant for added security. Once they hatch out, the blister beetle has an intricate life process. It goes through a number of larval phases, occasionally as much as 6 or 7, in the winter months. They come to be pupa in the springtime and become grownups in the very early summer season. Many species leave just a solitary generation each year.
- The larva of the blister beetle is occasionally referred to as parasitoid, due to the fact that it takes a living host to feed on up until it has sufficient power to get to the following phase of its life process. Unlike a real bloodsucker, nonetheless, this constantly leads to the fatality of the host. The larva is rather mobile after hatching out, which allows it to locate an ideal host. It comes to be much less mobile as it calms down and grows, however the grown-up comes to be very mobile once again in order to take a trip in between blossoms.
- The hazardous cantharidin produced by the beetle has actually been generally utilized by lots of societies as a lotion (for gout arthritis or joint inflammation), an aphrodisiac, or a growth cleaner. This therapy is occasionally called Spanish fly, due to the fact that the contaminant is originated from the species of the exact same name.
Species, Kind, and Scientific Name
The family name of the blister beetle is Meloidae. It’s not specifically clear what this name describes, however it was believed to be initial called in 1810 by the Swedish entomologist Leonard Gyllenhaal (that, surprisingly, was a forefather of the stars Jake and Maggie Gyllenhaal). There are some 7,500 acknowledged species around the world spread throughout lots of various category. Well- well-known participants of this family consist of the red- headed master beetle of Arizona, the black blister beetle of The United States and Canada, and the 3- candy striped blister beetle, additionally from The United States and Canada. Many species do not have a name past the scientific name; they’re improperly comprehended and under- researched.
Appearance: Exactly How to Recognize Blister Beetles
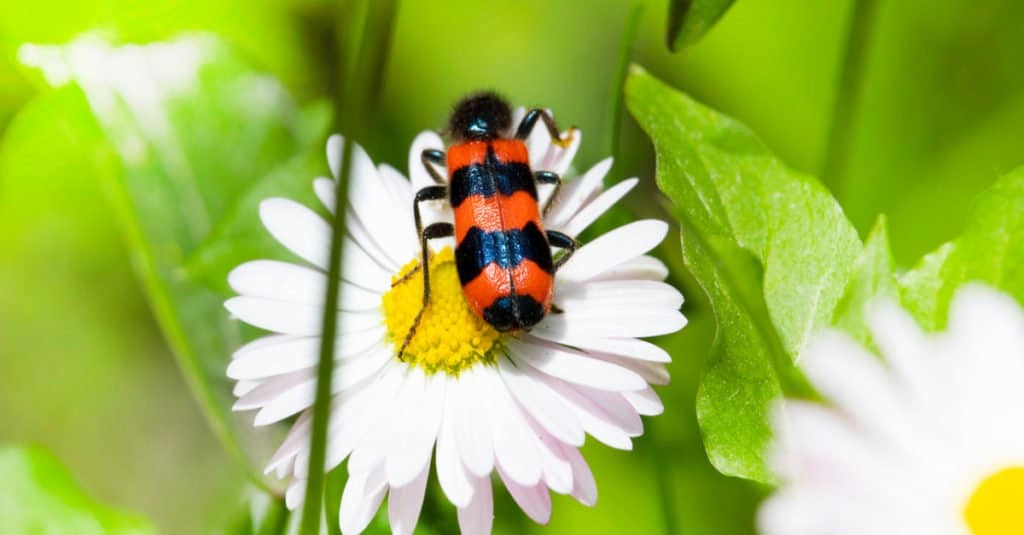
The blister beetle differs a fair bit in shapes and size, however a lot of species are characterized by a vast head, a slim thorax (the belly), and a long, round, or round- like abdominal area. They have 2 sets of soft wings, in plain comparison to the difficult front wings of a lot of beetles. The blister beetle introduces its poisoning with a vivid grow. Versus a black or grey base, a lot of their bodies have intense red, eco-friendly, or yellow markings to indicate their risk to possiblepredators The red- headed master blister beetle of Arizona is among the biggest species, determining greater than an inch long. The majority of them are very little bigger than a coin.

studiomirage/Shutterstock. com
Environment: Where to Locate Blister Beetles
The blister beetle is located in virtually any type of cozy or warm environment worldwide with an adequate quantity of blooming plants to feed upon.
Diet:
The blister beetle is normally omnivorous. It eats both insects and plant issue throughout its life time.
What consumes the blister beetle?
The blister beetle is preyed upon by a multitude of various creatures, birds, reptiles, and frogs. Nevertheless, the uncomfortable contaminant is a powerful deterrent for any type of would certainly- be killer that hasn’t progressed any type of defense versus it.
What does the blister beetle eat?
The feeding routines of the blister beetle modification throughout its life process. As a larva, the beetle eats premature bees or grasshopper eggs, occasionally adhering to a grown-up back to their nest. As a grown-up, the beetle eats the blossoms, nectar, and leaves of plants. Their most usual targets consist of decorative and veggie plants.
Avoidance:
Blister beetles do not position much of an issue for many people, however they can occasionally make themselves a hassle for farmers and garden enthusiasts by harmful plants and plants. Farmers need to search for indicators of blister beetle task regularly throughout the collecting period. Once they’re well- developed, the blister beetles are difficult to get rid of. Luckily, they will typically unite in huge collections out near the side of the area, making them simpler to find. They are specifically drawn in to alfalfa plants and weeds, although they additionally feed upon tomatoes, potatoes, peppers, eggplants, and various other veggies.
As long as you’re just managing a tiny yard, the very best method to manage their numbers is to get the blister beetles by hand (with handwear covers on for defense) and put them right into a tiny container. Huge- range invasions are far more challenging to manage and might demand making use of chemical pesticides. An additional service is to alter the timing of the harvest prior to the blooming brings in the beetles to the area. If they in some way wind up lodged in the hay, after that there are a couple of possible remedies. Binding hay without kinking typically permits them to leave the hay with no damages. Raking the hay will certainly additionally get rid of a few of the blister beetles.