” Their scratchy tune seems like an automobile engine that will not begin.”
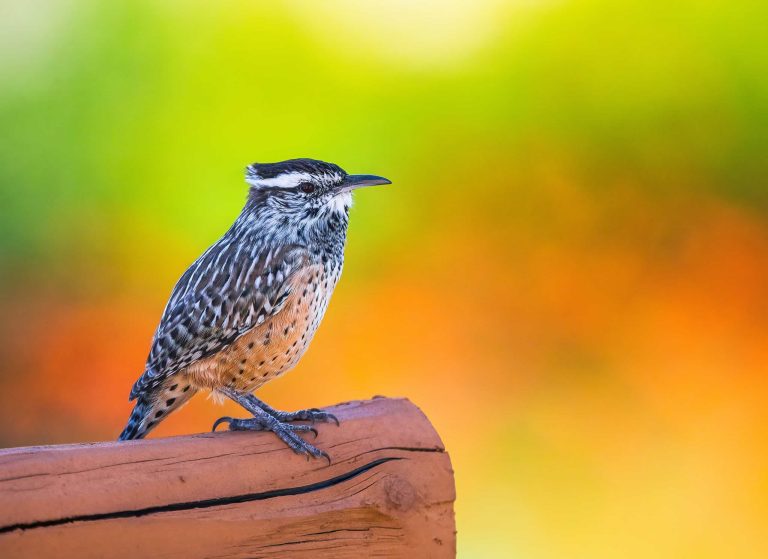
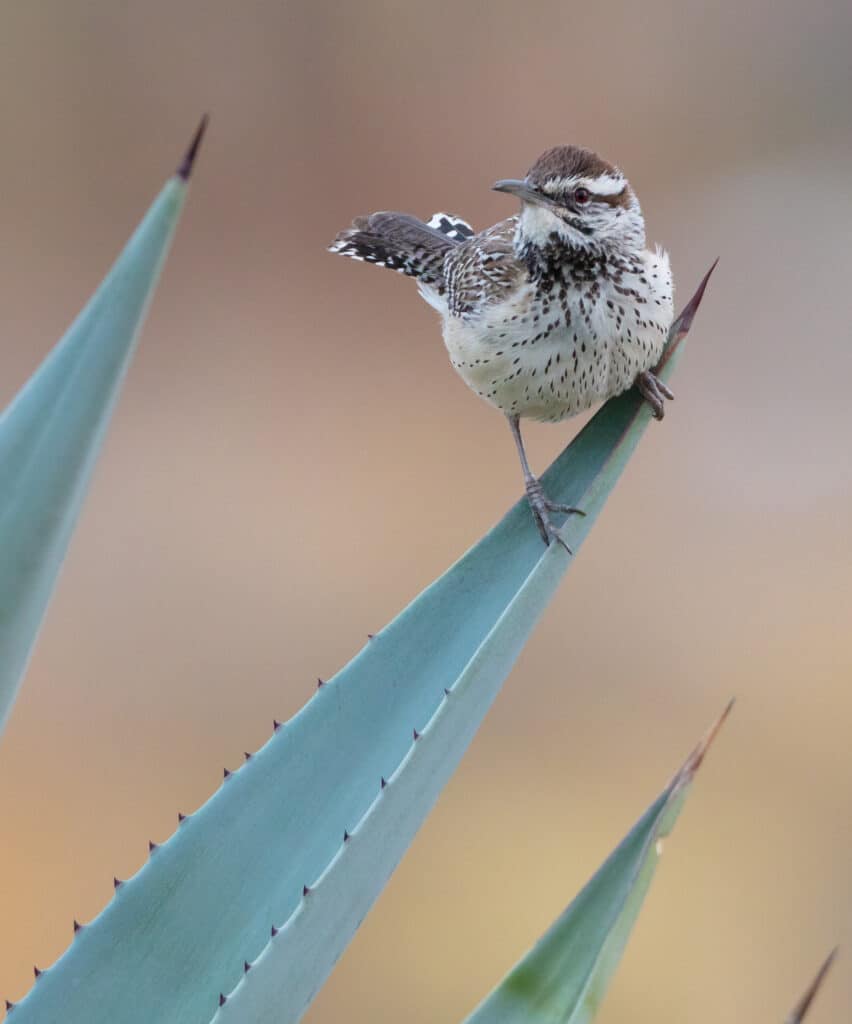
If you have actually ever before gone with a desert route in the Southwestern USA, you might have had a scratchy, mechanical serenade. The cactus wren is a staple in these desert atmospheres, whether set down on cacti or jumping about on the completely dry, messy ground. These desert birds are properly adjusted to stay in severe atmospheres; find whatever that makes the cactus wren special!
5 Fantastic Cactus Wren Truths
- The cactus wren is non- migratory and develops long-term residencies.
- They construct football- designed nests to discourage predators.
- It is the biggest wren in the USA, expanding 7.5 inches long.
- It will certainly eat dead insects off of vehicles.
- They create long-term set bonds forever.
Where to Discover the Cactus Wren
The cactus wren is just in the USA and Mexico. You can discover it in 6 states, consisting of The golden state, Nevada, Arizona, Utah, New Mexico, and Texas. In Mexico, it lives in Sonora, Sinaloa, Chihuahua, Coahuila, Hidalgo, Nuevo León, and Baja The golden state. This bird stays in dry and semi- desert areas, that include the Sonoran and Chihuahuan deserts. They are non- migratory and develop long-term regions, reluctant to leave also throughout seasonal adjustments. Additionally, they are remarkably territorial and will certainly safeguard their environments with vitality, noisally declaring when you have actually exceeded the border.
This wren stays in a selection of reduced, completely dry environments, generally deserts with tough hedges and cacti. Their favored is the cholla cactus, mesquite brush, and yucca. You will certainly probably see them in sets or family members, jumping in brush or parading on the ground.
Cactus Wren Nest
Females pick the nesting place, and males take part with the structure. You can discover their nests 3 to 10 feet in the air in desert plants like cholla cacti, acacia, and mesquite, bordered by thorns. The nest is football- formed with passage entryways, and the duo utilizes yard and plant fiber to structure it. It’s normally 7 inches in size and 12 inches long, considering concerning 6 ounces. Its special form is developed to be simply huge sufficient for them to press with yet little sufficient to maintain predators out. They line the within their nest with plumes, making it a soft, comfy, and protect area to hatch out chicks.
Scientific Name
The cactus wren’s ( Campylorhynchus Brunneicapillus) genus is Campylorhynchus, which is Greek for “bent beak,” and its byname brunneicapillus equates to “brownish hair.” Its usual name defines its tendency for setting down, nesting, and concealing in numerous cacti in desert environments. There are a number of subspecies of cactus wren yet researchers typically just acknowledge 7; every one of them drop within its recommended array in The United States and Canada.
Dimension, Appearance, and Actions
As the biggest wren in the USA, it is in between 7.1 and 7.5 inches long, considers 1.18 to 1.65 ounces, and a wingspan of 11 inches. This beefy bird has a long, durable beak, a long, rounded tail, and short, rounded wings. Its costs contours somewhat downwards and has to do with the very same dimension as its head. The cactus wren has a general brownish shade with white and black flecks, with unique long, white brows. Males and females look alike, yet juveniles are paler with brownish eyes as opposed to red.
The majority of wrens are timid and like to conceal in plants, yet cactus wren are social, loud, unbothered animals. They constantly make their visibility understood exposed, noisally calling and fanning their tail plumes. This species is versatile and interested, constantly discovering brand-new food resources, also choosing dead insects off of vehicles. They are not solid leaflets, so you will certainly probably see them getting on the ground or reduced hedges foraging for food.

Melinda Fawver/Shutterstock. com
Diet
The cactus wren is largely an insectivore, yet as an interested forager, it will certainly attempt numerous points.
What Does a Cactus Wren Eat?
The cactus wren generally consumes spiders and insects, such as ants, wasps, beetles, butterflies, and grasshoppers; It will periodically eat little reptiles like lizards. Around 20% of their diet originates from plant product, like berries, seeds, nectar, and cactus fruits. As a desert species, this wren seldom consumes alcohol complimentary- standing water. Rather, it obtains the majority of its hydration from the food it takes in, largely cactus fruit and sap. The cactus wren feeds its chicks a diet of entire insects, normally grasshoppers.
Predators, Risks, and Conservation Status
The IUCN checklist the cactus wren as “least concern,” suggesting it has a huge array and does not come close to the standard for an endangered species. Nevertheless, its populace is decreasing, though not dramatically, and it deals with feasible future concerns from environment modification. The cactus wren might be especially conscious dry spell, wildfires, and springtime warm front. Severe warm and dry spell impact their young and can trigger food scarcities, and wildfires have the prospective to spoil their environments.
What Consumes the Cactus Wren?
Like the majority of birds, the cactus wren should handle anything bigger with claws and teeth. Its predators consist of hawks, coyotes, foxes, bobcats, and residential cats. Their football nests are to shield them and their young.
Recreation, Youthful, and Molting
Cactus wrens develop virginal set bonds, and the pair protects their year- rounded residence with each other. Their communications are special. They offer each various other a welcoming event, where they spread their wings and offer an extreme phone call. Egg laying happens 18 days after copulation, and the males develop “dummy” nests when the female is nurturing.
They normally lay 3 to 4 eggs, and incubation takes 16 days (only by the females). Wrens might ruin eggs from close-by nests yet are not understood for brood parasitism. As soon as hatched out, both moms and dads feed the nestlings, and the young leave about 19 to 23 days after hatching out. Nevertheless, they will certainly continue to be in their moms and dad’s area up until they are in between 30 and 50 days old.
Populace
The cactus wren’s international populace is 8.5 million fully grown people. This species has a descending trending populace, with a typical decrease price of 2.1% each year (from 1970 to 2017). Nevertheless, brief- fad information suggest their numbers have actually decreased by 19% over the previous years. Some research studies suggest they might require supplementary food to enhance reproductive success.
Up Following:
.