The fire salamander is the very best- understood salamander in Europe and a typical species of salamander in Central and Southern Europe.
As a center to a huge- sized and highly constructed salamander, it is so well- understood not just as a result of its frequency however intense caution shades and dangerous fluid spray. Its name originates from the old idea that it originated from fire. As an unique- looking amphibian, it is likewise typically maintained as a pet.
5 Amazing Fire Salamander realities!
- It is just one of Europe’s biggest salamanders.
- Numerous subspecies are dangerous.
- Its intense shades alert predators that it threatens.
- Females bring to life live salamanders, unlike various other species.
- It conceals under logs, and when individuals collect the logs to make a fire, it goes out — — thus, its name.
Fire Salamander Scientific name
The fire salamander comes from class Amphibia (amphibians), Order Urodela (lizard- like amphibians), Family Salamandridae (real salamanders and newts). It comes from the genus Salamandra, which has 6 species of salamanders located in main and southerly Europe, North Africa, and Western Asia.
The scientific name of the fire salamander is Salamandra salamandra, with S. salamandra salamandra (discovered fire salamander) being the choose subspecies or species kind. There are 13 subspecies. 2 subspecies ( fastuosa and bernadezi) are viviparous, indicating the young create inside the mom and are birthed online, while the remainder are ovoviviparous, indicating the young create in eggs inside the mom till they prepare to hatch out.
4 previous subspecies are currently identified as distinctive species after special realities developed from hereditary study:
- S. algira – Bedriaga, 1883– African fire salamander
- S. corsica – Savi, 1838– Corsican fire salamander
- S. infraimmaculata – Martens, 1885– Near Eastern fire salamander
- S. longirostris – Joger & & Steinfartz, 1994– south Iberian fire salamander
Fire Salamander Appearance
The shades of the fire salamander are largely black with yellow spots and areas, although in specific subspecies orange and red might change or blend right into the yellow. Males and females are alike in appearance, other than throughout the reproducing period when the males have an inflamed gland around their air vent, which consists of a spermatophore. It expands to a size of 15– 30 centimeters (6- 12 in), however typically just gets to fifty percent of that and a weight of regarding 40g (0.09 pounds).
A center to big- sized salamander species, it has actually a highly constructed body. One more particular, per its Subfamily Salamandrinae, is the harsh skin and absence of rib or costal grooves alongside their bodies. In Europe, it is the biggest salamander species.
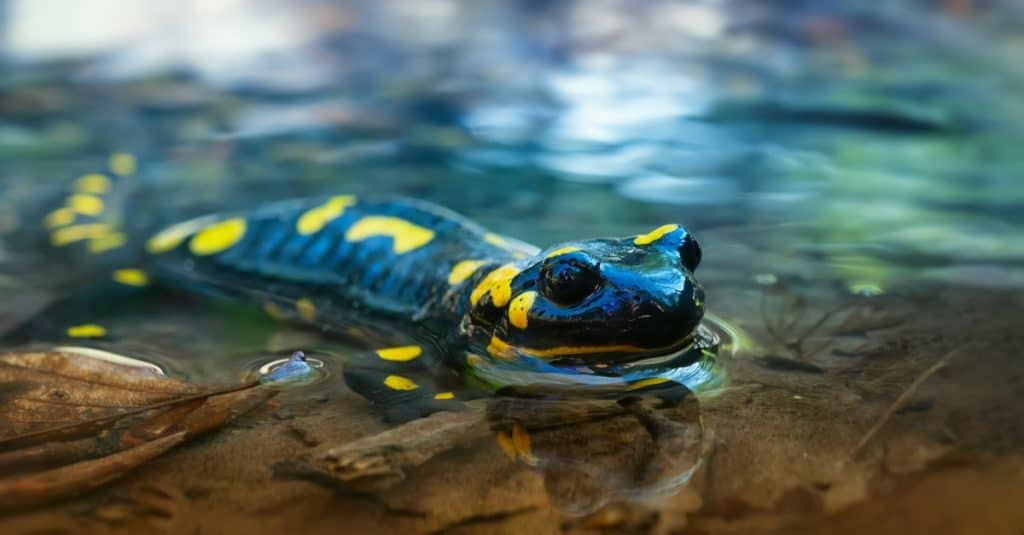

Fire Salamander Actions
The habits of the fire salamander is greatly singular. A reclusive amphibian, it favors to conceal under logs, leaves, various other items, and around mossy tree trunks. It is nighttime, being energetic at night and in the evening, however they are diurnal when it rainfalls.
Fire Salamander Environment
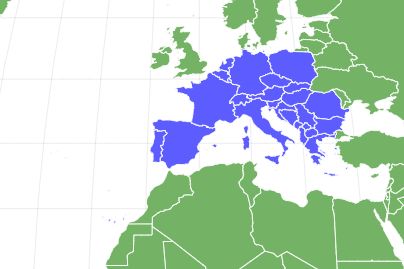
The all-natural environment of these animals is the woodland, its biome being deciduous, uneven woodlands and chain of mountains in Europe, North Africa, and cooler locations of the Center East. Tiny creeks, streams, or fish ponds are required in its biome so they can saturate themselves. It lives at elevations in between 250 meters (820 feet) and 1,000 meters (3,300 feet) and hardly ever as reduced as 25 meters (82 feet).
- S. s. alfredschmidti (Asturian Fire Salamander): Iberian.
- S. s. almanzoris (Almanzor Fire Salamander): High elevation, Sistema Hills of Central Spain.
- S. s. bejarae: Reduced elevation, Sistema Hills of Central Spain.
- S. s. bernardezi: Iberian.
- S. s. beschkovi: Bulgaria.
- S. s. crespoi: Iberian.
- S. s. fastuosa or S. bonalli (yellow- candy striped fire salamander): Iberian
- S. s. gallaica (Galician fire salamander): Iberian.
- S. s. gigliolii: Italy
- S. s. morenica: North Africa.
- S. s. salamandra (discovered fire salamander): Balkans.
- S. s. terrestris (prevented or grouped fire salamander): Landmass Europe, northwest Africa, and the Mediterranean shore.
- S. s. werneri: Bulgaria.
Fire Salamander Diet
The fire salamander’s diet is meat-eating. It preys upon insects, spiders, earthworms, slugs, newts, and young frogs. In bondage, its diet includes crickets, mealworms, waxworms, and silkworm larvae. When capturing target, it utilizes its teeth or tongue to order them.
Fire Salamander Predators and Hazards
These animals has couple of all-natural predators, as a result of the toxic substances in its skin, which can upset or eliminate predators, in addition to the fluid spray it generates when intimidated. Toxic substance glands are focused around its head, dorsal skin surface area, and tail. Its main alkaloid contaminant, samandrin, creates solid muscle mass convulsions, high blood pressure, and hyperventilation in all animals. Grass snakes have actually been understood to eat grown-up fire salamanders, while various other predators like to capture the young. Bigger reptiles, hawks, and eagles might periodically prey upon the fire salamander if are immune or create a resistance to its toxic substances.
The most significant risk to these animals is the Bsal fungi ( Batrachochytrium salamandrivorans), which was mistakenly presented from Asia by individuals importing Oriental newts to market as pets. This lethal fungi makes it difficult for them to take in oxygen with their skin or eat. Because its exploration in 2013, Bsal has actually eliminated countless indigenous salamanders in Europe.
Fire Salamander Reproduction and Life Process
These animals have 2 various types of reproduction in their subspecies. 2 subspecies ( fastuosa and bernadezi) are viviparous, indicating the young create inside the mom and are birthed online. Every one of the various other subspecies are ovoviviparous, indicating the young create in eggs inside the mom till they prepare to hatch out. Unlike various other species of salamanders, they bring to life live young however still live near tiny creeks, fish ponds, or streams in order to saturate themselves.
Reproducing period starts in springtime and lasts till fall, most usual throughout late springtime and very early summertime, with breeding ashore biomes. Those subspecies staying in warmer environments, such as between East, friend in between October and January. Pregnancy typically occurs throughout hibernation for 2- 5 months. Fire salamander reproduction is sex-related, with the male challenging the female and obstructing her course, after that scrubing her with his chin to share passion. He after that gets her front arm or legs with his very own, down payments a spermatophore (which consists of a sperm package), and tries to reduce the female to obtain her cloaca touching it. If effective, the female attracts the sperm package and feeds the eggs inside her body.
The eggs create inside and when they are hatching out, the female down payments them right into the water in those subspecies where the larvae are not birthed online. She can bring to life 20- 75 young with approximately 20- 30. The young reach sex-related maturation at 4- 6 years.
The common life expectancy mores than 6- 14 years with a typical optimum of three decades however can measure up to half a century in uncommon instances. In bondage as a pet, its life expectancy is typically 6- 14 years with approximately one decade.
Fire Salamander Population
The varieties of these animals are secure and provided as Least Concern according to the IUCN. Nevertheless, study on approximated population dimensions is required.