” Rapid, effective and serene participants of the African environment.”
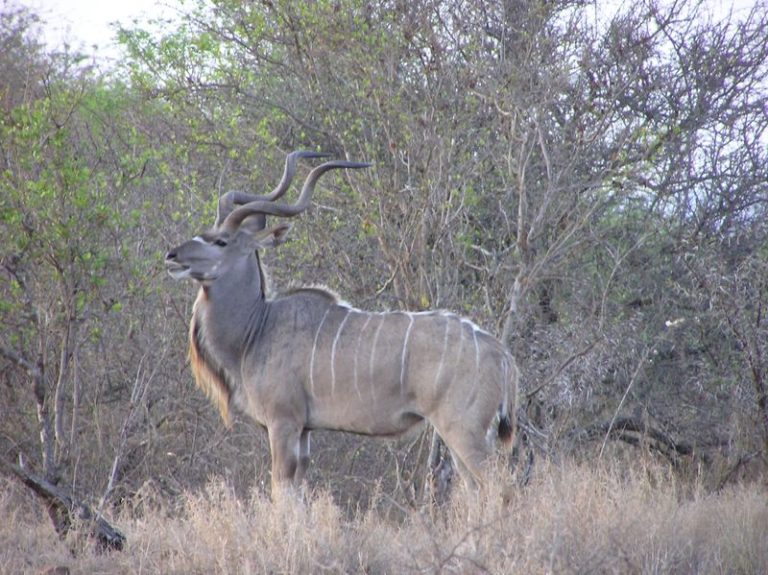
The name kudu explains 2 various antelope species, called better kudu and minimal kudu, that are discovered in southerly and eastern areas of Africa. Both kinds are characterized by the lengthy, turning horns that expand on the heads of fully grown males. They likewise share similar environments, body framework and pigmentation, although there is remarkable distinctions in dimension in between the better and minimal species. The kudu is an animal with easy grazing practices and all-natural camouflage to aid them prevent being conveniently found by the numerous predators in their indigenous environment.
An Extraordinary Animal: 3 Kudu Truths!
- Broadband: The kudu is an animal that can get to rates of over 60mph when trying to get away from a killer.
- Ritualistic horns: The animal’s spiraled horns are valued in neighborhood spiritual techniques and are likewise made right into music tools.
- Courteous competitors: Despite the fact that males in some cases take part in rutting, they are usually not really fierce when completing for companions.
Kudu Scientific Name
Kudu, additionally meant koodoo, is stemmed from the name provided to the animal by the neighborhood, nomadic Khoikhoi, that are native to southwestern Africa. The better kudu is identified as Tragelaphus strepsiceros and the minimal kudu is Tragelaphus imberbis The genus Tragelaphus shares its name with a word initially presented by the old Greek thinker Aristotle in his dental representation of a visualized animal that was half goat and fifty percent deer.
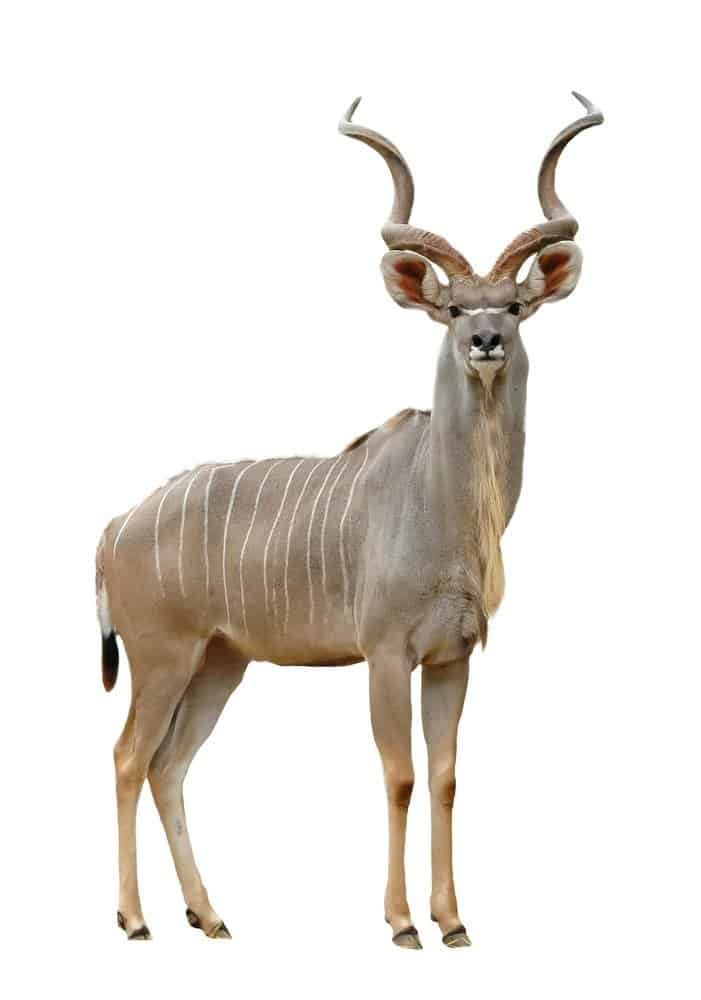
Kudu: The Animal’s Appearance
Both species have similar body framework and percentages, although there are a couple of remarkable distinctions in their outside attributes. Both have grey to brownish hair that is damaged by a collection of white red stripes and various other markings, commonly consisting of a chevron noticeable on their nose. The minimal species commonly has in between 11 and 15 white red stripes on their body, while the better species normally has in between 6 and 10.
Body dimension is among the crucial distinctions in between both species. The minimal species is usually 3 to 3.5 feet high and considers in between 130 and 230 extra pounds. Greater kudu can get to a lot better dimension, with a possible shoulder elevation of approximately 5 feet and complete weight of fully grown grownups varying in between 260 and 600 extra pounds. The biggest bull male on document evaluated in at over 690 extra pounds.
All male kudu have the possible to expand spiraled horns that can be fairly lengthy pertinent to their body dimension. Lower kudu males can expand horns that depend on 3.5 feet long, while some better kudu have actually been reported showing off horns as long as 6 feet. These horns have a tendency to make 2 to 3 big spins as they incline in reverse from the head towards the incurable factor, which establishes them besides the snugly wound horns seen on various other antelopes.

Kudu Actions
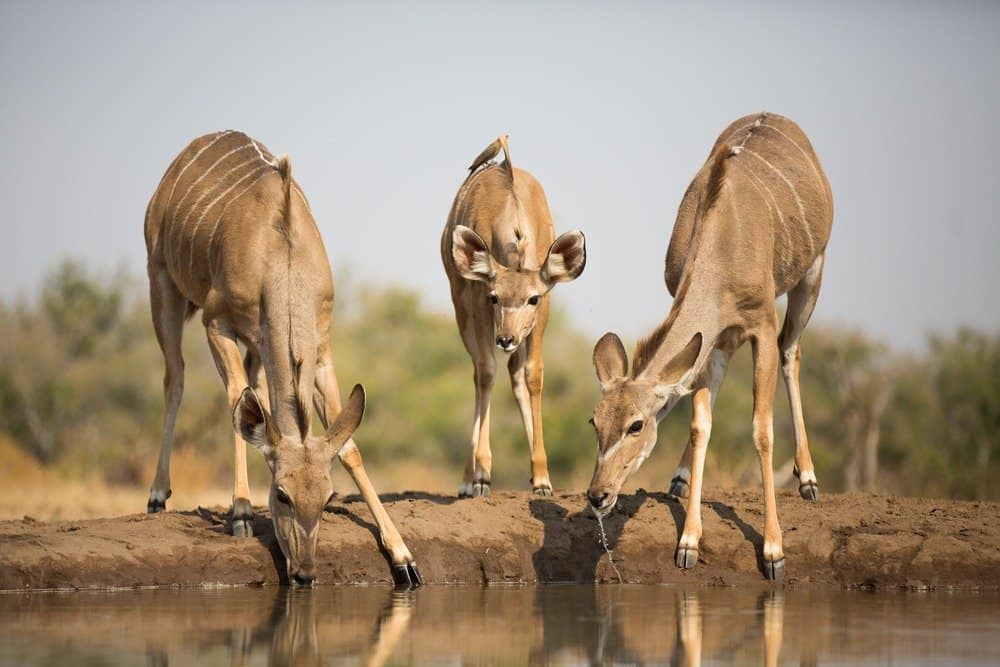
As herbivores, the majority of the kudu biology and actions is tailored towards making it through in a possibly severe indigenous environment and staying clear of harmfulpredators They have a tendency to remain really still as they forage, which permits their pigmentation to give efficient camouflage. They are most energetic throughout the evening or early morning hrs and look for sanctuary in thick brush throughout the daytime. Kudu commonly take a trip in tiny packs or herds, however they are likewise often seen alone. Just like various other sort of antelope, these animals have a solid trip response and can relocate really swiftly when challenged with a prompt hazard.
Kudu: The Animal’s Environment
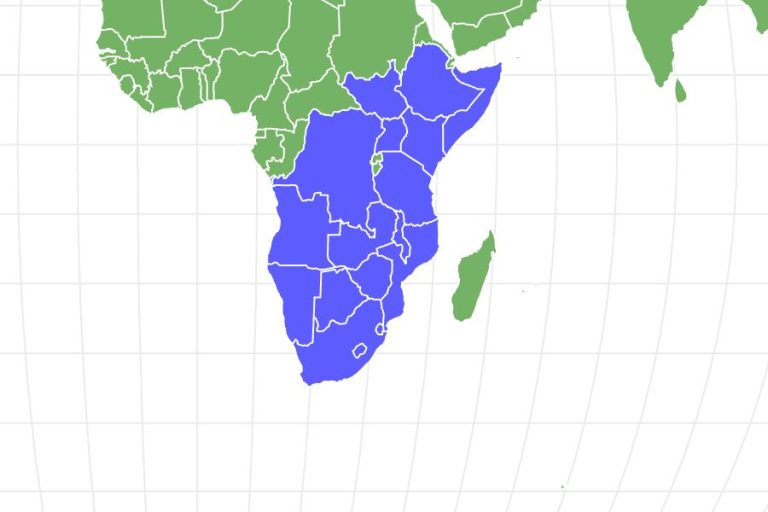
Both kudu species are belonging to southerly and eastern sections of Africa. Greater kudu have a much better geographical distribution that consists of components of Ethiopia, Tanzania, Kenya and as much southern as South Africa. There are likewise some separated populaces of the cottoni subspecies discovered in main Africa. Lower kudu have a much smaller sized distribution and are just discovered in eastern areas near the Horn of Africa, consisting of Ethiopia and Kenya.
These animals have solid leaping and bulldozing possible, which assists them browse sturdy surface around hillsides or hills and build frankly via thick brush and development in woody areas. They have a tendency to live in timberland and forested locations, especially along water resources. Lower kudu are a little bit much less water reliant than their better relatives. Both species can please several of their water requires by seeking particular sorts of plants as they forage.
Kudu Diet
Kudu are versatile foragers that take in a wide variety of plant products in timberland, thicket and open areas. Lower kudu are recognized to have a diet that is mainly vegetation from trees and hedges, with the majority of the staying being from creeping plants and similar plants. Nonetheless, kudu can likewise eat tender young shoots, plant origins and might also target some sorts of fruit when they can locate them. Delicious plants that keep water are likewise a prime target throughout the completely dry period. Kudu in bondage are commonly fed yard or alfalfa hay together with some all-natural forage and enriched pellets or biscuits.
Kudu Predators and Hazards
The kudu share their indigenous variety with numerous singular and pack predators that position a substantial hazard to their survival. Maybe one of the most harmful predators allow cat species, consisting of lions, cheetahs and leopards. Felines have a tendency to utilize a mix of stealth, perseverance and rate to assail the quick- acting kudu while they forage. Packs of seen hyenas and African searching dogs are likewise recognized to catch or find kudu as target.
Humans are both a killer and significant ecological hazard to the lengthy- term practicality of kudu populaces. Individuals search the animals for their meat, big hides and identified horns, which are generally made use of to make music, decorative and different house items. Indigenous environments, specifically of minimal kudu, are likewise intimidated by the ongoing development of human negotiations and development of business farming ventures throughout the area.
Lesser kudu are especially vulnerable to environment fragmentation and searching because of their tiny geographical distribution, which has actually triggered their classification as near threatened. They can likewise experience considerable population losses from transmittable conditions like rinderpest, which has actually annihilated numbers in the past. Greater kudu have a much larger indigenous variety and are taken into consideration a species of least concern by guardians.
Kudu: The Animal’s Reproduction, Infants, and Life-span
Some herbivores can obtain rather fierce throughout mating period, however kudu are amongst the much more serene species on the continent. Males commonly complete by flaunting their dimension in account till one withdraws. Nonetheless, they might literally battle by securing horns if among the rivals does not pull back. Triumphant ales commonly duke it out females at first after that follow them for some time prior to in fact mating.
Females stay expectant for regarding 240 days prior to bring to life a solitary calf bone, which commonly considers around 10 to 15 extra pounds. Moms different from their team prior to they provide their infant. They leave the calf bone thoroughly concealed in the brush while they forage throughout the clenched fist 4 or 5 weeks after birth. At this moment, calf bones come with the mom on foraging explorations till it has to do with 6 months old.
Regardless of the treatment and interest that mom kudu reveal their young, about fifty percent of calf bones pass away prior to the 6 month mark. Scientists approximate that just regarding 1 in 4 people make it to 3 years of ages. Kudu get to sex-related maturation within a couple of years, however males are seldom effective at mating till they have to do with 4 or 5 years of ages. Apart from high fatality prices throughout young people, the animals commonly live to be 10 to 15 years of ages in the wild and approximately 20 in bondage.

Kudu Population
Scientists approximate there are much less than 100,000 minimal kudu staying in Africa. Their restricted indigenous variety incorporated with considerable environment interruption by humans is a severe reason for worry. Concerning a 3rd of them presently reside in National Parks and various other secured locations.
Specific population numbers for better kudu are unidentified, although the incredibly restricted variety of the cottoni subspecies, discovered just in Chad and Sudan, indicates maybe a prospect for endangerment.
Animals in the Zoo: Where to locate the Kudu
The Smithsonian’s National Zoo has a tiny population of kudu readily available for site visitors to observe. They reported the birth of a male kudu calf bone in 2019. Over a loads various other city and state zoos throughout the nation, consisting of the Maryland Zoo, likewise have minimal kudu on display screen for interested visitors.