” A natterjack toad can injure to 7500 eggs in a solitary clutch”
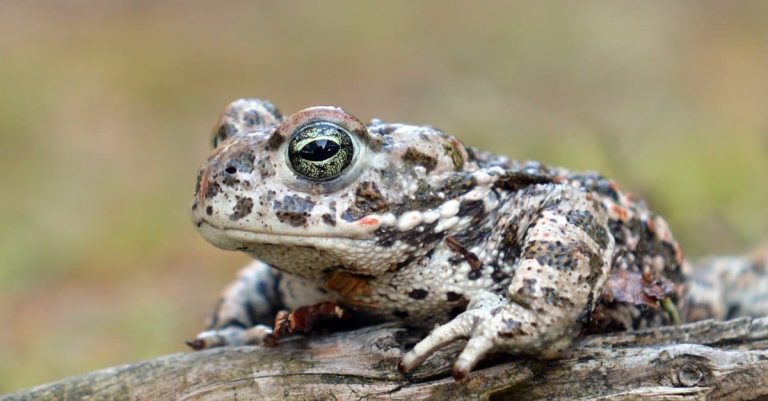
The natterjack toad is belonging to Europe. It looks a whole lot like a common toad with the exemption of an upright yellow line on its back. It’s predator consuming woodlice, worms, and spiders. These amphibians are energetic in the evening seeking victim. Their life-span is 15 to twenty years.
5 Extraordinary Natterjack Realities!
- This amphibian is called the running toad due to the quick method it creeps rather than jumps
- The noise of its loud telephone call can take a trip as much as 3 miles
- They have a life expectancy rising to twenty years
- They stay in an environment with marshes and dune
- This amphibian display screens the exact same shades of a common toad yet with a yellow red stripe down its back
Natterjack Scientific Name
The natterjack toad’s scientific name is Epidalea calamita Words Epidalea is the genus of this toad while the significance of words calamita is magnetic. This describes the idea that the moon and its magnetic pull attracts, European toads (like magnets) to superficial fish ponds throughout breeding period.
The label of this amphibian is the running toad due to the method it relocates. This label does not have an actual significance behind it. Though this amphibian does not in fact run, it relocates so quickly it appears like it’s running! It belongs to the Bufonidae family and remains in the Amphibia class.
Natterjack Appearance & Habits
The protuberance- covered skin of a grown-up natterjack includes a combination of shades consisting of environment-friendly, brownish, and lotion. The recognition of this amphibian is conveniently done by seeking the yellow red stripe down its back. This is just one of its most evident attributes. Its back legs are additionally much shorter than a common toad’s hindlegs.
At 2 to 3 inches long, natterjacks are smaller sized in dimension than common toads. A 3- inch natterjack is equivalent in size to one and a fifty percent golf tees. Additionally, common toads can expand to be 6 inches in dimension. The heaviest a natterjack can consider is a little over half an ounce.
Though this amphibian is simply 3 inches long at one of the most, it has some defenses versuspredators For one, its dark shades permit it to mix well right into its marshy environment. Additionally, it can expand its body and extend its legs to make itself show up bigger. This can be adequate to terrify some predators away. On top of that, a natterjack has glands on its head that launch a milklike toxin. When gotten by a killer like a hedgehog or a heron, the natterjack launches toxin creating the killer to allow go. Once it gets on the ground, the amphibian can escape rapidly by relocating its one-of-a-kind crawling stride.
One more protection of this amphibian is it is energetic in the evening. Relocating under cover of darkness can aid this toad to stay concealed and secure from every one of the predators energetic throughout the day.
Natterjacks are singular with the exemption of the reproducing period when these amphibians collect at superficial fish ponds. A team of toads is called a knot. Reproducing period is when the unique male breeding telephone call can be listened to for as much as 3 miles. Some individuals believe their telephone call seems like an ‘‘ emergency room, emergency room’ noise. If you enjoy a male natterjack contact us to females, its neck broadens right into a bubble to send out the telephone call also better right into the range. This is just one of those truths you practically need to attend think. Additionally, you would certainly need to ask a male natterjack for the precise significance behind its odd- appearing telephone call.
Usually talking, these amphibians have a timid nature, concealing in marsh turf and under rocks up until it’s time to head out and search for food in the evening. They aren’t hostile animals.
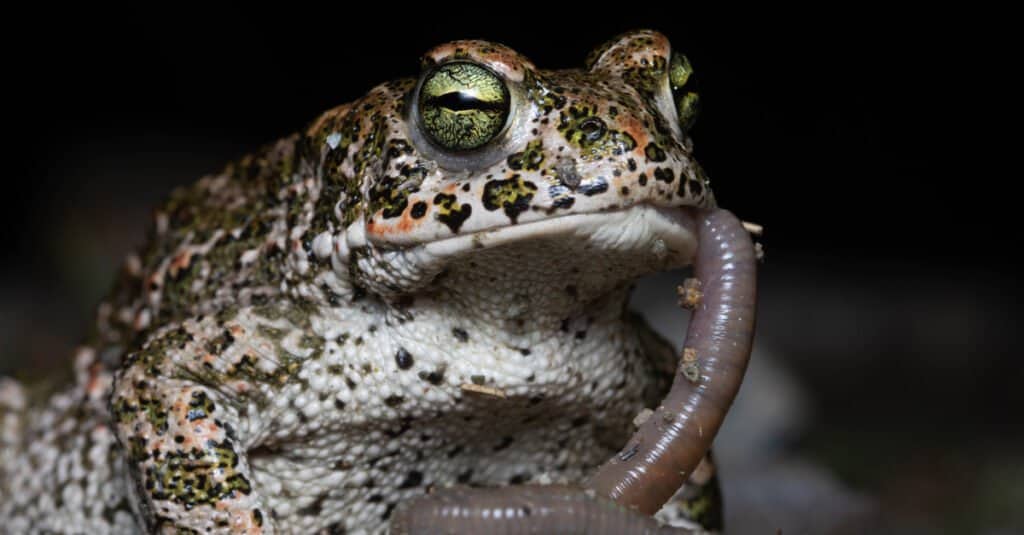

Natterjack Environment
The natterjack is a European toad. It stays in the seaside locations of Spain, England, France, Ireland, and Germany, among others. Their environment consists of dune, marshes, and marshes. They collect at superficial swimming pools of cozy water throughout breeding period. This is where they mate and where females lay their strings of eggs.
If you were seeking this amphibian in a marshy location, you ‘d possibly discover some hiding under rocks due to the fact that these animals like to dig in the soft sand. Or, you might see a couple of sticking their direct out of the marsh water. Nevertheless, these little animals assimilate so well with the dark water and greenery around them, you can be taking a look at one and not also understand it!
These amphibians are nighttime, so they are out searching and calling each various other in the evening. They have large eyes and slim students providing great vision after the sunshine goes away. They require great vision to record the insects they require to nurture themselves.
Natterjack Predators and Risks
The life process of a natterjack has numerous phases consisting of egg, tadpole, adolescent, and grownup. A natterjack in the tadpole phase consumes marine greenery while a grownup is a predator consuming insects of several kinds.
What does a natterjack toad eat?
Natterjacks eat spiders, woodlice, worms, snails, and various other little insects. These amphibians conceal underneath marshy plants waiting to record insects going by.
What consumes natterjack toads?
Herons, hedgehogs, and foxes are a few of the predators of this little amphibian. These animals share the exact same environment as the running toad and search for food in or near the water. These predators are most likely to eat this amphibian’s tadpoles and eggs also.
In regards to preservation, natterjacks are provided as Least Concern yet with a lowering population. Their numbers are decreasing in component as a result of environment loss. Their environment is decreasing as an outcome of farmland growth and all-natural adjustments in the landscape. They are additionally in danger of a lethal condition called chytridiomycosis. Chytridiomycosis takes a trip rapidly amongst teams of amphibians. This condition is researched by taking a look at the cells of a dead amphibian.
Natterjack Reproduction and Life Process
The reproducing period of this toad starts in March or April and proceeds right into the summer season. Males kind huge teams or knots, around superficial fish ponds. From there, they ask for female friends by making a loud, scratchy noise. These amphibians have numerous companions throughout a reproducing period.
Female toads lay eggs in the cozy superficial water. This is one more among those truths to aid you with recognition. While common toads lay 2 strings of eggs, a natterjack toad lays simply one. However, that a person string can have up to 7500 eggs! When the eggs are laid the female leaves her young. It takes 8 to fifteen days for the eggs to hatch out relocating this toad to the following action in its life process.
As a note, male natterjacks have actually been understood to rest beside superficial swimming pools where eggs are laid. Some biologists think these males are standing guard over the eggs and tadpoles. If a smaller sized killer goes along, a male expand its body in an initiative to terrify the trespasser far from the vulnerable eggs.
Natterjack toad infants called tadpoles are much less than an inch in dimension. Among the factors this amphibian lays numerous eggs exists’s a great chance great deals of the eggs or tadpoles will certainly be consumed by fish, frogs, and various other predators The even more tadpoles there are, the better the possibility some will certainly make it through enough time to become grown-up natterjacks.
Tadpoles are much less vulnerable to passing predators than the eggs of this amphibian. Tadpoles have the ability to conceal amongst the drifting greenery in a superficial fish pond and take in marine plants for nutrients.
The life process of this toad from egg to adolescent takes around 8 weeks. The life-span of this amphibian is 15 to twenty years.
Natterjack Population
The population of this amphibian is unidentified. It’s provided as Least Concern yet is lowering in number. Worldwide of European toads, it’s taken into consideration unusual.